How can remote sensing help to save sea lions?
The motivation: Steller sea lions are iconic marine mammals that play a vital role in ocean ecosystems. However, their populations have been declining in recent years due to a variety of factors, including climate change, pollution, and human activities. Accurately counting sea lions is essential for conservation efforts, but traditional methods of counting are time-consuming and often inaccurate. New technologies like deep learning and aerial photography make it possible to count sea lions more accurately and efficiently than ever before.
The method: To count sea lions from aerial photography, we employed deep learning with density maps. Density mapping is a technique that utilizes deep learning algorithms to generate heat maps of animal density in images. By analyzing these heat maps, we were able to accurately estimate the number of sea lions in the images, even when the animals were partially obscured or overlapping.
To achieve this, we trained a deep learning model in a supervised manner using hundreds of aerial sea lion images that were annotated by a human expert. The images were collected by NOAA Fisheries Alaska Fisheries Science Center and included different categories of sea lions such as adult males, sub-adult males, adult females, juveniles, and pups. By training the deep learning model on this diverse dataset, we were able to achieve high accuracy in sea lion counting.
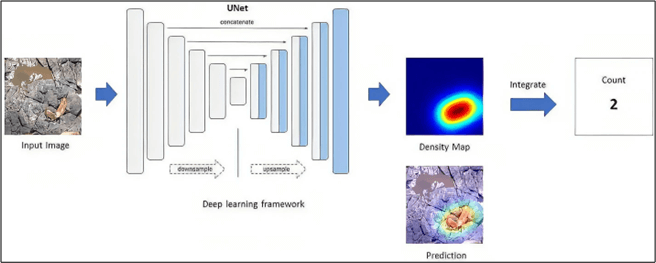
The results: We trained a deep learning model to count Steller sea lions, employing a novel feature extractor technique to improve overall accuracy. To evaluate the model’s prediction accuracy, we measured the Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) between the predicted and actual animal counts. The results of our experiments were highly encouraging, with the model achieving an impressive RMSE of 1.88. This indicates that our model was able to accurately count Steller sea lions in challenging conditions, including complex backgrounds, varying illumination conditions, and heavy overlapping and occlusion of the animals.
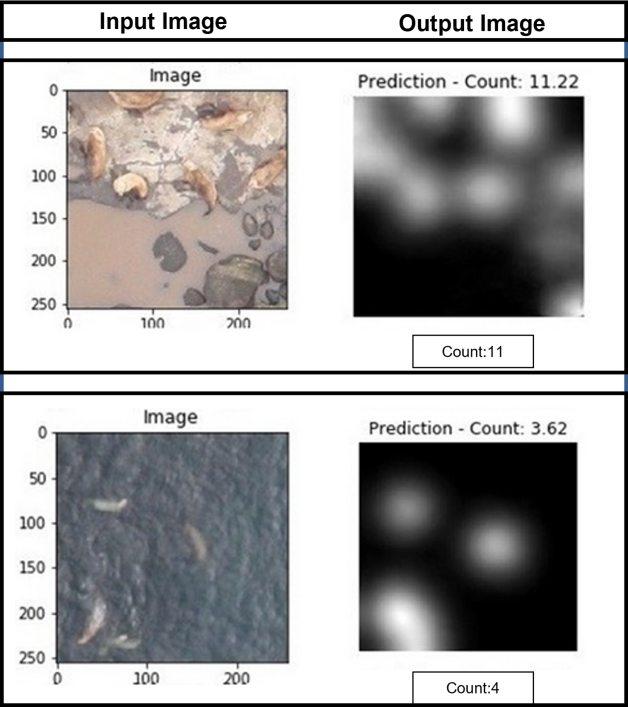
The importance: Wildlife conservation efforts are critical, however traditional population monitoring methods can be time-consuming, labor-intensive, expensive, and error-prone. Nonetheless, aerial photography together with advanced computer vision AI techniques has shown significant potential for accurately and efficiently counting Steller sea lions. These techniques can significantly contribute towards the conservation of many other terrestrial animals. Aerial surveys complemented by deep learning offer a faster and more accurate way of estimating populations, providing a revolutionary new approach to wildlife conservation.
The Perspective: Remote sensing, together with computer vision, present a promising solution for wildlife population monitoring, offering the potential to reduce the amount of time and effort required while also increasing the accuracy of estimates. This technology has significant implications for conservation efforts, enabling the monitoring and protection of endangered and threatened species in a more effective way. Large-scale studies following these technologies/techniques can effectively contribute to the long-term survival and biodiversity conservation of endangered and threatened species.
Chirag Padubidri, Andreas Kamilaris, Savvas Karatsiolis and Jacob Hamminga, Counting Sea Lions and Elephants from Aerial Photography using Deep Learning with Density Maps, In Animal Biotelemetry Journal, vol. 9, no. 27, August 2021. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40317-021-00247-x